DoS - Exploiting WAF Request Size Limits
Reference
Overview Published in June 2024 by zhero_web_security, this blog post introduces a technique to bypass Web Application Firewall (WAF) request size limits, enabling a targeted Denial of Service (DoS) attack. Inspired by a NahamCon 2024 talk on WAF bypasses, it exploits parameters reflected in cookies to make websites inaccessible to victims via malicious cookie values.
Key Concepts
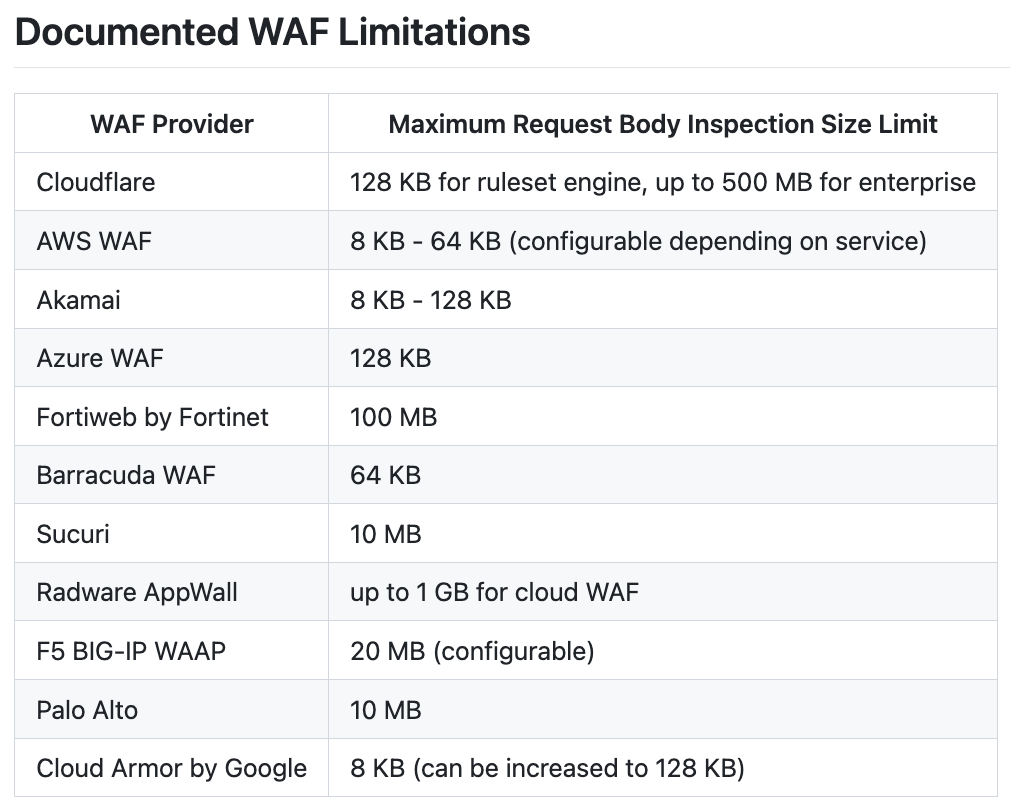
WAF Request Size Limits: WAFs limit inspection to a default size (e.g., AWS WAF skips analysis for oversized requests) to optimize performance, allowing bypasses by inflating request sizes.
Parameter Reflection in Cookies: User-supplied parameters (e.g., for tracking/marketing) are often echoed in Set-Cookie headers via POST requests without CSRF protection.
Targeted DoS Mechanism: Malicious payloads in cookies trigger WAF blocks on subsequent requests, resulting in 403 errors and site inaccessibility for the cookie's duration (e.g., 1 month). WAFs typically do not inspect responses, enabling the payload to pass initially.
Methodology
Prerequisites: Identify targets with:
WAF-protected sites using default inspection limits.
POST-transmitted parameters reflected in cookies.
No CSRF protection on the endpoint.
Attack Steps:
Craft a POST request with a large dummy parameter (exceeding WAF limit) followed by a malicious payload (e.g.,
' OR SLEEP(10);--) in the reflected parameter.Host an HTML page with JavaScript to send this request to the target (e.g., via fetch or form submission).
The server sets the malicious value in a cookie, bypassing WAF response inspection.
Victim's future requests include the cookie, triggering WAF blocks.
Variations: Can be combined with XSS for automated delivery without victim interaction on attacker-controlled sites.
Findings/Exploits
Bypass Effectiveness: Relies on common WAF configurations (e.g., AWS WAF's disabled response inspection by default).
Impact: Achieves persistent DoS per victim, requiring cookie deletion for mitigation. High prevalence due to widespread WAF bypass vulnerabilities and common parameter reflection.
Proof-of-Concept: Demonstrated with SQLi-like payloads; adaptable to other injection types.
Limitations: Requires victim to visit attacker's page; not fully remote without XSS.
References:
WAF Bypass Tool: https://github.com/assetnote/nowafpls
NahamCon Talk: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0OMmWtU2Y_g
Last updated
