OAUTH Misconfigurations
Brute Force to Get Legacy OR Unimplemented OAuth Flows
Modify hd= parameter
hd= parameterRemove email from scope
email from scopeUse Access Token Of Your App Instead Of Auth Token Of Victim App
Change The Host Header
Insert Your Domain In Referer Header While
Insert admin@comapny.com in scope
IDOR in id= Parameter
id= ParameterAdd JSON OR XML Extension To OAuth Endpoint
XSS in OAUTH Connect/Callback
Insert XSS Payloads To Cause Errors
SSTI in Scope Parameter
XSS in RedirectUri
Path Traversal to open Redirect
Authentication Bypass via OAuth Implicit Flow
Forced OAuth Profile Linking
CSRF

Insufficient Redirect URI Validation

Exploits:
Steps:
SSRF via OpenID Dynamic Client Registration
Stealing OAuth Access Tokens via a Proxy Page
OAuth Account without email Address
Microsoft nOAuth Misconfiguration
Facebook OAuth Misconfiguration
OAuth Code Flaws
Access Token Scope Abuse
Pre-Account Takeover
ALL ATTACKS WITH PROMPT=NONE TO MINIMISE INTERACTION
PROMPT=NONE TO MINIMISE INTERACTION

Play With response_mode
response_mode Exploit XSS in the Authorization Server to steal Victim's code

POST-AUTH REDIRECT + LOGIN CSRF

Disclosure of Secrets
Client Secret Brute Force
ATO via OAUTH Hijacking
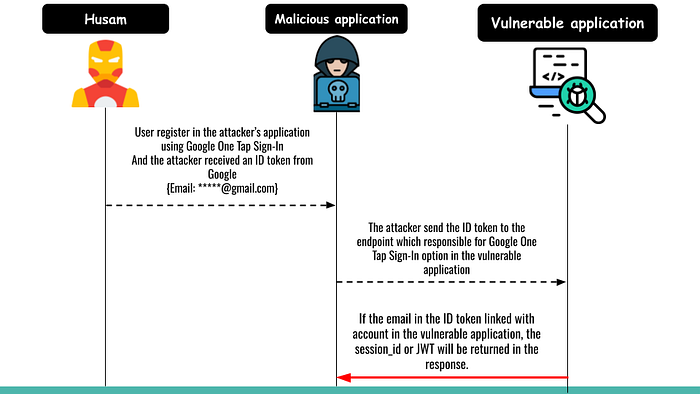
Referrer Header Leaking Code + State
Access Token Stored in Browser History
Everlasting Authorization Code
Authorization/Refresh Token Not Bound to Client
Refresh Token Issues
Race Conditions in OAuth 2 API Implementations
Summary
References
List Of Patterns To Bypass The Whitelist In Redirect URL Parameter
Use IDN Homograph Attack To Spoof Redirect URL Parameter
Black Characters
Change Request Method
Race Condition
XSS in the code= parameter
code= parameterReuse The Authorization Code With XSS Payloads
Use The OAuth Token With Logged In User In OAuth Provider
Exploit Post Messages
ATO Using OKTA SSO Misconfiguration
Token Reuse Attack
Last updated